Yoonji Han Aug 8, 2022
On December 21, 1816, a group of fifty white elites gathered in a Washington, D.C. hotel to discuss the future of freed Black Americans.
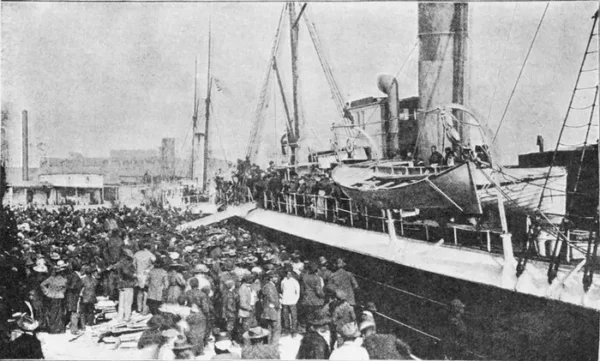
Following the American Revolution, the number of freed Black Americans had grown from 60,000 in 1790 to 300,000 by 1830. The American Colonization Society emerged as the solution, with the mission of shipping Black people to a colony in Africa.
The organization was the brainchild of the Reverend Robert Finley, a Presbyterian minister from New Jersey. The ACS’ early supporters included some of the nation’s most powerful and influential men, including Henry Clay, Daniel Webster, and Francis Scott Key, as well as slave-owning US presidents Thomas Jefferson, James Monroe, and James Madison.
“Can there be a nobler cause than that which, while it proposes to rid our country of a useless and pernicious, if not a dangerous portion of our population, contemplates the spreading of the arts of civilized life?” Clay said in his opening address.
Colonization, the state-sponsored emigration and resettlement of freed Black Americans outside America, was widely supported in the US for religious, economic, and social reasons. Even after its dissolution in 1964, the ACS has left a lasting legacy of segregationist sentiment in both America and abroad, according to historians.
“The establishment of the American Colonization Society was a watershed moment in American history,” Eric Burin, a history professor at the University of North Dakota, said. “What you have is a powerful white organization propounding a vision of America as a white person’s country, and African Americans responding with a resounding rebuttal that it’s their country, too.”
This article appears in its entirety at the Insider website. It can be read here.